Project Description
Author: Sarkar et al.
Summary:
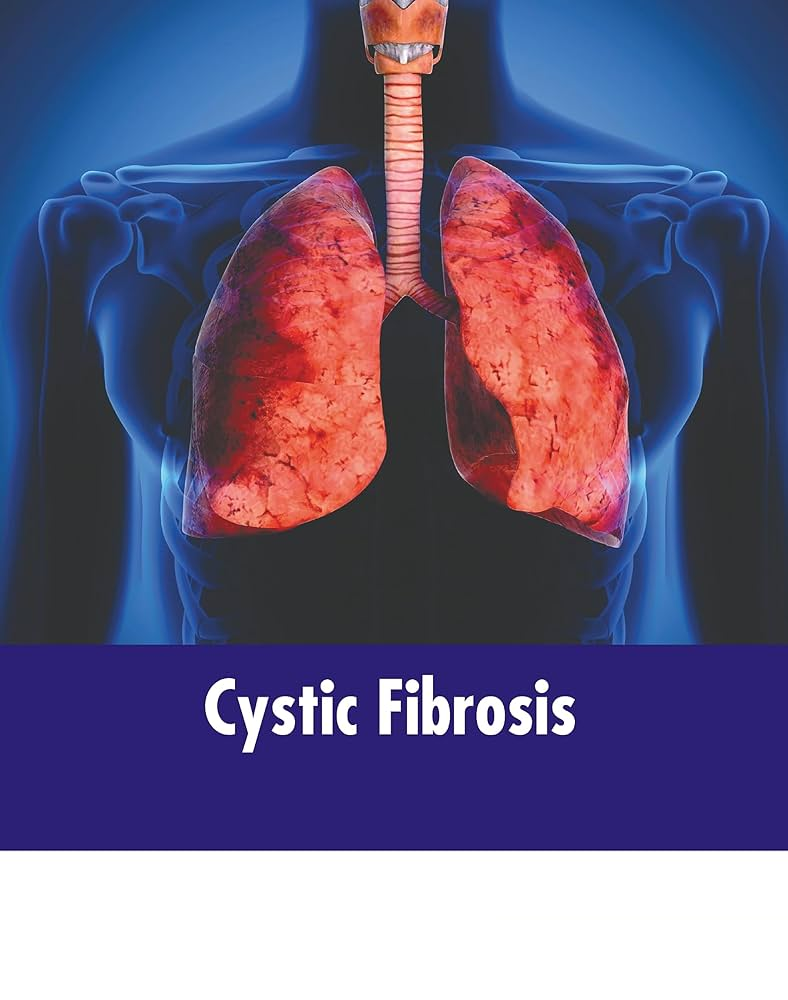
Infection control in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients plays a crucial role in improving the survival of patients with CF. Antimicrobial sensitivity patterns in these patient groups in our country are currently lacking. Therefore, the purpose of the study was to evaluate the microbiological cultures and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of pediatric CF patients.
A total of 50 respiratory samples were prospectively collected from the period between February 2021 and October 2021. Sputum and oropharyngeal swabs were processed for culture and microbiological testing. Sample collection and evaluation were performed according to the Good Laboratory Practice guidelines (GLP). Informed written consent was ensured before participation. Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS v 26.
The median age of the children was 30 months (6–120) months, with a male predominance (66% vs 34%). Single and two organisms were isolated in 72% (n = 36) and 12% (n = 6) of cases, respectively. During the study period, 36% of the patients harbored Pseudomonas aeruginosa, 18% harbored Klebsiella pneumoniae, and both Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli were detected in 16% of cases. Levofloxacin was found to be the most active antibiotic agent with 100% susceptibility. In contrast, nearly all isolates were resistant to amoxicillin, erythromycin and rifampicin.
Levofloxacin is the most effective agent to treat CF patients. Active surveillance of the resistance pattern should always continue to be promoted.
Status: Completed and published
Full text link: https://epag.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s43054-022-00127-w
Keywords: Cystic fibrosis, CF, Antimicrobial sensitivity, Antimicrobial resistance, Infection control. Pediatric patients, Microbiological cultures