Project Description
Author: Pandit et al.
Summary:
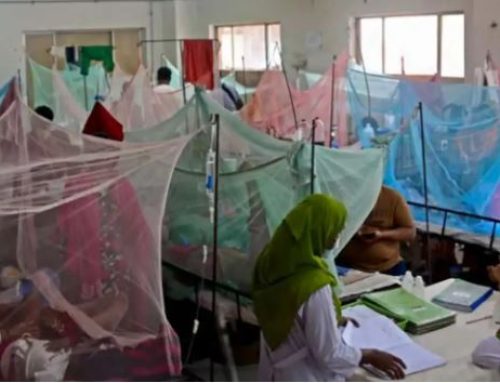
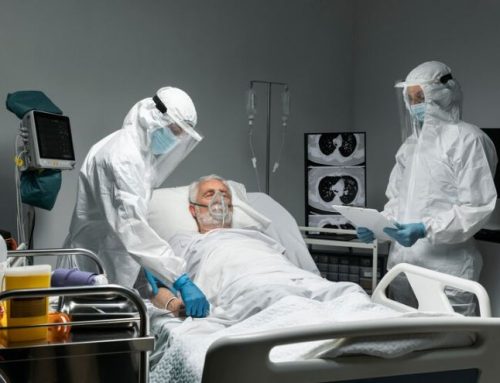
A prudent allocation of resources towards public health yields significant benefits, such as enhanced quality of life, increased life expectancy, and improved physical and mental well-being for the entire nation. Presently, South Asian countries are experiencing a shift in disease patterns, necessitating a postpandemic overhaul of their healthcare systems. This review examines the economic ramifications of investing in public health from the perspective of South Asian nations.
Existing global evidence demonstrates a positive correlation between health expenditure and economic growth in numerous studies. However, certain communities have observed contrasting or diminished economic outcomes despite health expenditures. These inconsistencies can be attributed to factors such as inadequate adherence to investment policies, political and systemic corruption, inequitable resource distribution, and an insufficiently skilled workforce. Addressing the significant gaps in public health services in South Asian countries must be prioritized to ensure a healthy population.
Investing in public health can lead to improved management of public health issues, potentially fostering competent human capital and stimulating economic growth. Nonetheless, any factors that impede economic progress in relation to public health investment must be earnestly addressed at the national level.
Status: Ongoing
Full text link: Not available